


KONSTANTINOS S. GALANAKIS / CEO of Elvictor Group
A Modern Architect of Human-Centered, Digitally Driven Crewing Konstantinos S. Galanakis stands as one of the most distinctive voices in today’s global manning and crewing landscape. At a time when the maritime industry is racing to modernize—balancing digital transformation, regulatory pressure, and the welfare of seafarers—he has developed a rare, practitioner-driven perspective that blends operational experience, human-centered leadership, and a deep respect for the Filipino maritime workforce.

What is anchor? An anchor is a heavy device, typically made of metal, that is used to connect a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the vessel from drifting due to wind or current. Purpose ‣To Hold the Vessel in Place It secures the ship in a fixed location, especially when it is not at a dock or port. ‣To Prevent Drifting It stops the vessel from being carried away by wind, waves, or currents. ‣To Provide Safety in Emergencies In case of engine failure or rough weather, the anchor helps prevent the ship from drifting into danger. ‣To Assist in Positioning During Operations Useful for activities like dredging, diving, or repairs where stability is essential. 1. Fluke Anchor (Danforth) The Fluke anchor, also known as the Danforth anchor, is a lightweight, high-holding power anchor designed with two wide flat flukes that pivot on a shank. Purpose: It is ideal for anchoring in sandy or muddy bottoms, where its broad flukes can dig in deeply and hold firmly. Key Features: ‣Made of high-strength steel or aluminum ‣Lightweight and easy to handle ‣Excellent holding power relative to its weight ‣Commonly used on smaller vessels, yachts, and recreational boats 2. Plow Anchor (CQR) The Plow Anchor, commonly known as the CQR anchor (short for Coastal Quick Release), features a single plow-shaped fluke that pivots on a shank, resembling a farmer’s plow. Purpose: Designed to penetrate and bury itself in a variety of seabeds, it is widely used for general-purpose anchoring, especially in changing conditions Key Features: ‣Heavy-duty forged or cast steel construction ‣Hinged design allows it to adapt to shifting loads ‣Performs well in sand, mud, gravel, and some grassy bottoms ‣Often seen on cruising and commercial vessels 3. Bruce Anchor The Bruce anchor, also known as the Claw anchor, is a one-piece anchor with a claw-like shape designed to dig into the seabed and provide steady holding power. Purpose: Developed originally for offshore oil rigs, the Bruce anchor is now popular for small to medium recreational boats due to its reliable setting and holding capabilities. Key Features: ‣Made from forged or cast steel ‣One-piece construction with no moving parts ‣Performs well in sand, mud, and some rocky bottoms ‣Commonly used by cruising yachts and powerboats
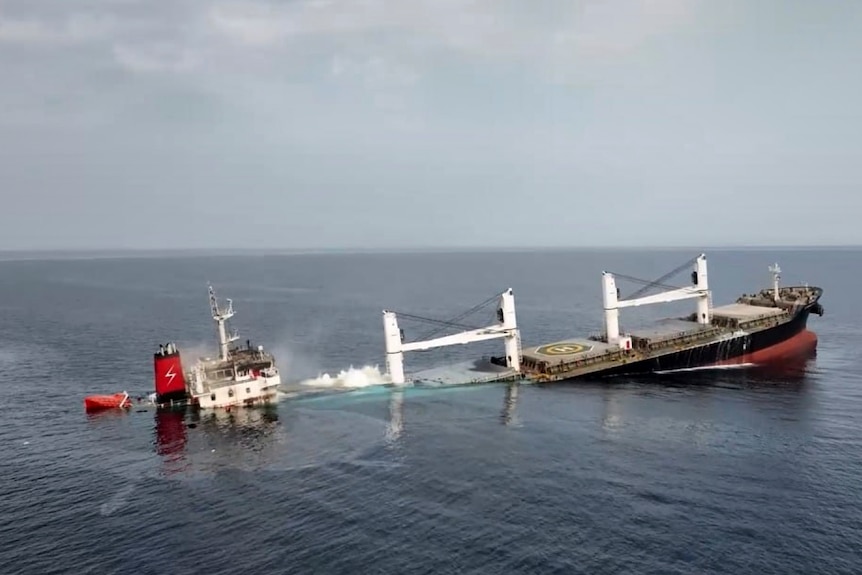

Nine Eternity C Crew Members Set for Release After Months in Houthi Custody
Nine Filipino seafarers held captive by Houthis after the July sinking of the cargo ship Eternity C will be released, the Philippine Department of Foreign Affairs (DFA) confirmed on Tuesday. The crew will be transferred from Sanaa, Yemen to Muscat, Oman before they return home, according to the DFA. The release is credited to diplomatic efforts led by the DFA together with the government of Sultanate of Oman. The Eternity C, a Liberia-flagged vessel, had been attacked by the Houthis with sea drones and rocket-propelled grenades in early July. The attack forced the crew to abandon ship; the vessel eventually sank. Rescue teams managed to pull several crew members from the water shortly after the attack. However, a number of seafarers remained unaccounted for. The Philippine government welcomed the news, expressing “sincerest appreciation” to Oman for its role in securing the safe release and repatriation of the sailors.
.jpg)
Tanker MIDVOLGA-2 Attacked in the Black Sea
The Russian-flagged tanker MIDVOLGA-2, carrying a cargo of sunflower oil, was attacked while transiting the Black Sea. The incident occurred approximately 80 nautical miles off the coast of Türkiye as the vessel sailed from Russia toward Georgia. Initial reports indicate that the vessel was struck by what is believed to be an unmanned aerial drone. Despite the impact, the tanker did not issue a distress signal and remained operational. All 13 crew members were confirmed safe, and the vessel continued its voyage under its own power toward the port of Sinop for inspection and further evaluation. The attack on MIDVOLGA-2 adds to a growing number of recent incidents involving Russian-linked tankers in the region, heightening concerns over maritime security and the overall risk environment in the Black Sea. Coastal authorities and maritime stakeholders remain on alert as investigations into these incidents continue.
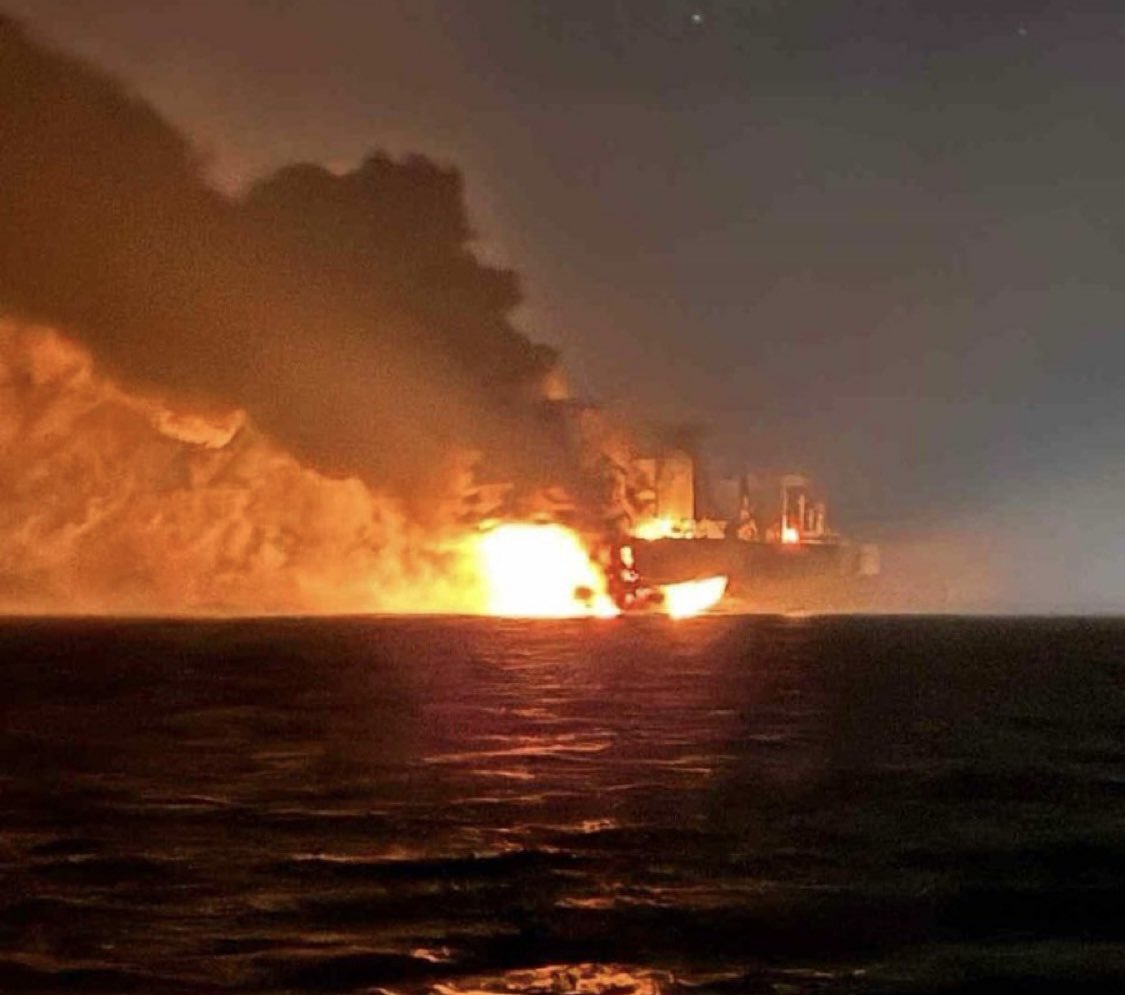

Black Sea Ship Insurance Jumps After Drone Strikes on Sanctioned Tankers
War-risk insurance for ships sailing in the Black Sea has risen sharply after two sanctioned oil tankers were hit by naval drones. The vessels, linked to Russia’s so-called “shadow fleet,” were heading toward the port of Novorossiysk when the strikes happened. Following the incident, insurers raised their rates for ships entering the region. Coverage for a week-long trip to Ukrainian ports increased to about 0.5% of a ship’s value. For ships calling at Russian ports, the cost climbed even higher, reaching between 0.65% and 0.8%. Insurers say the new prices reflect growing concerns that similar attacks could happen again.
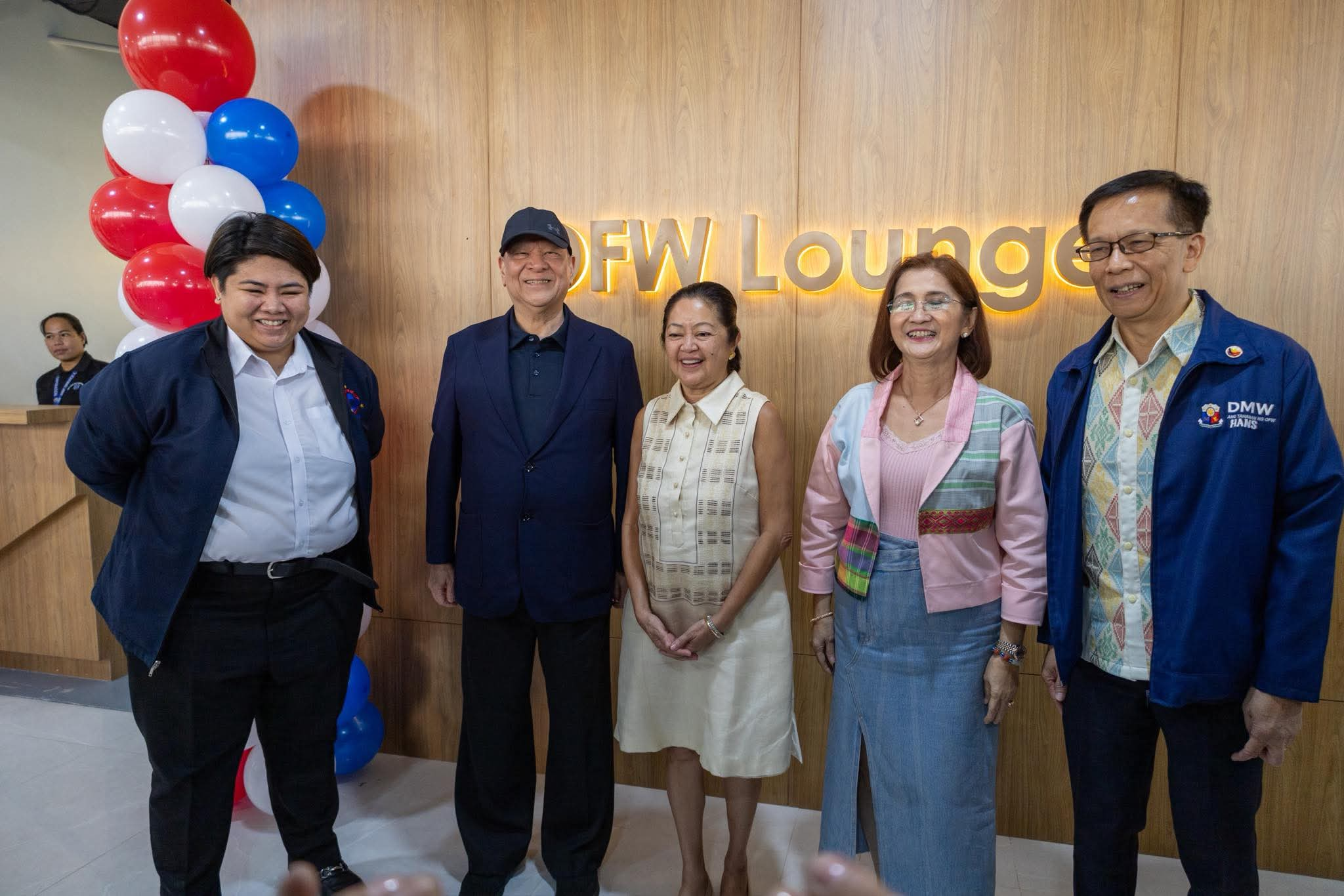

New OFW Lounge at NAIA Terminal 1 Officially Opens
The new OFW Lounge at NAIA Terminal 1 was formally inaugurated today, a significant step in enhancing the travel experience of Overseas Filipino Workers and reaffirming the government’s commitment to “Serbisyong May Puso.” The ceremonial ribbon-cutting was led by First Lady Louise Araneta-Marcos, joined by Department of Migrant Workers (DMW) Secretary Atty. Hans Leo J. Cacdac, OWWA Administrator Atty. Patricia Yvonne M. Caunan, Pasay City Mayor Imelda Gallardo Calixto-Rubiano, and NNIC Chairman & CEO Ramon S. Ang. Positioned as the government’s first holiday offering for OFWs, the newly opened lounge provides a more spacious, comfortable, and welcoming environment for Filipino workers departing through Terminal 1. With expanded amenities and improved services, the facility aims to offer greater convenience and a more dignified travel experience for the country’s modern-day heroes. The initiative underscores the administration’s continued efforts to uplift the welfare of OFWs and ensure they receive the care and support they deserve—from departure to their safe return home.
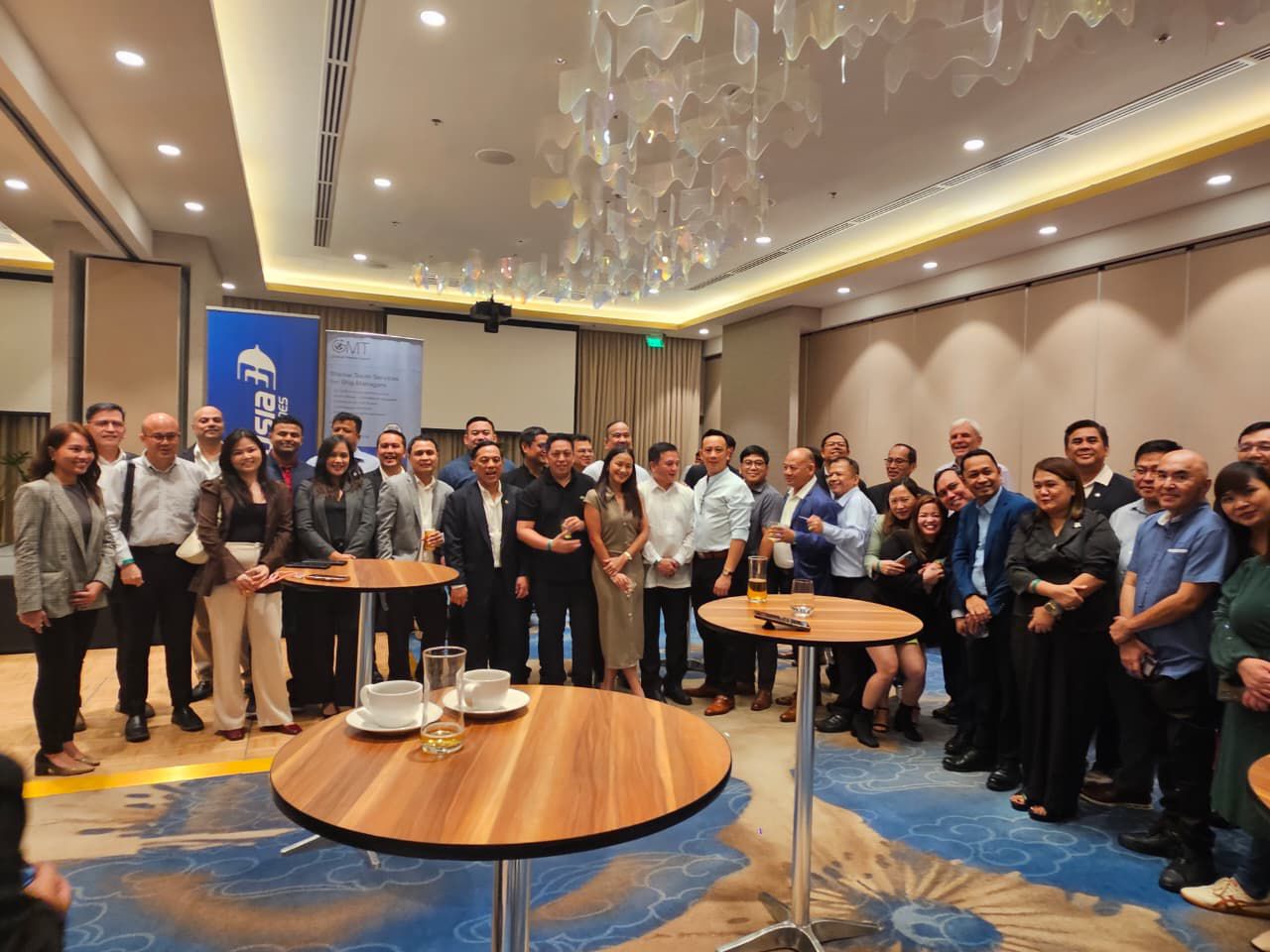





























The Managers’ Club (TMC) Christmas Party and Year-End Celebration
The Managers’ Club Christmas Party and Year-End Celebration, held at the elegant Levatine & Mediterranean Hall of Grand Westside Manila Bay, gathered maritime executives, managers, and industry professionals for an evening dedicated to unity, collaboration, and festive appreciation. Organized through the strong support and initiative of the Managers’ Club founders, and made possible by the generous contributions of its sponsors, the event provided a warm and vibrant setting for the maritime community to close the year together.
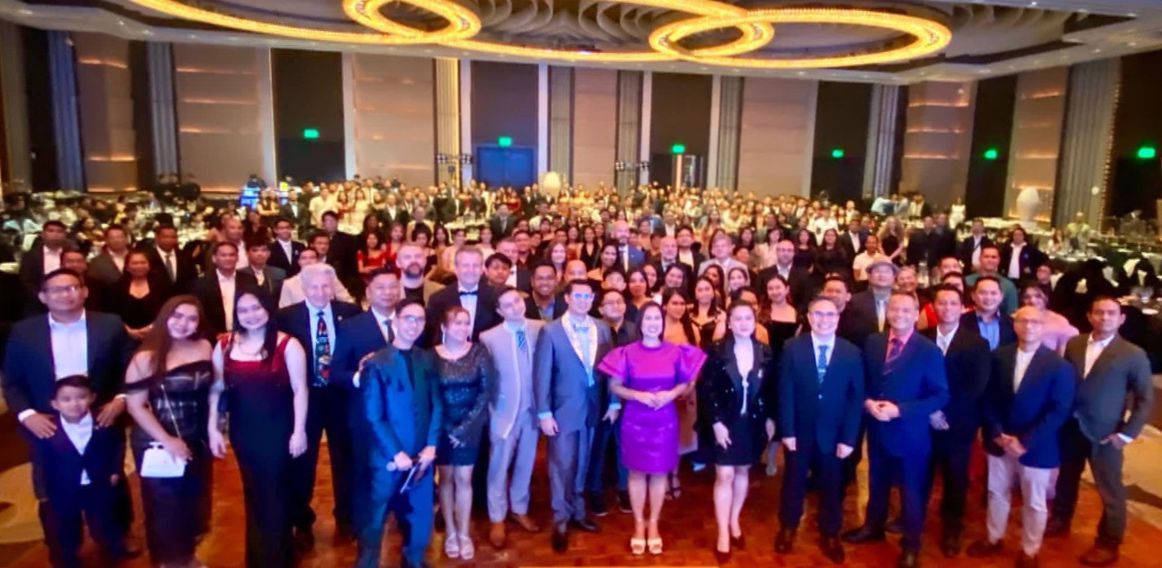

The Inter Maritime Group Hosts First Joint Year-End Celebration at The Manila Hotel
The Inter Maritime Group gathered its Philippine subsidiaries for the first-ever joint year-end celebration at The Manila Hotel’s iconic Fiesta Pavilion. The event brought together executives, maritime professionals, and industry partners representing the group’s three local entities: INC Navigation Company Philippines, Intership Crew Philippines, and the Intership Navigation Training Center, Inc.
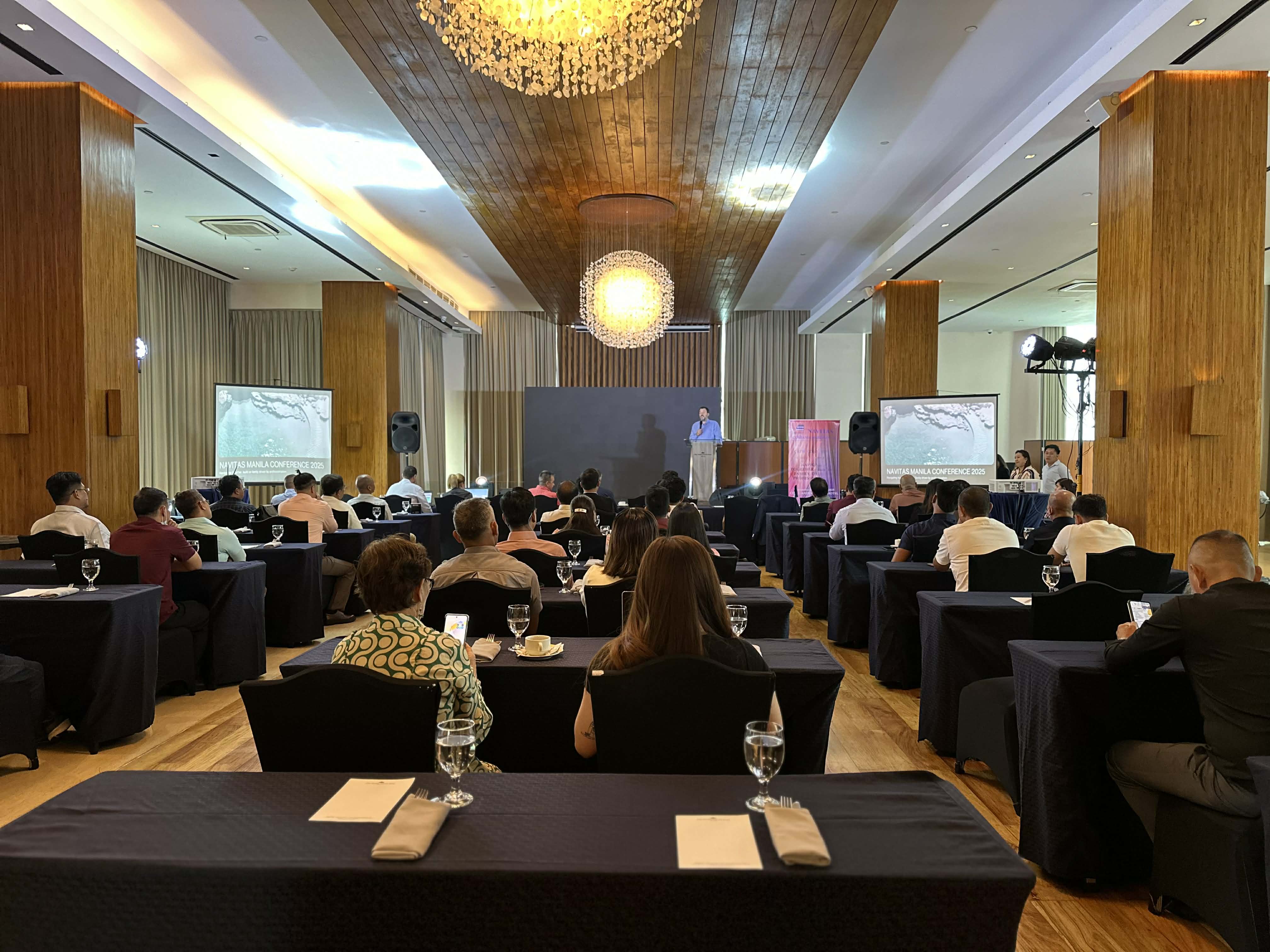

The Navitas Crew Conference 2025 has formally concluded at the City Garden Grand Hotel in Makati, bringing together seafarers, fleet personnel, and company leaders for a comprehensive program centered on the theme “Navigating Together – Built on Family, Driven by Professionalism.” Held at the Rosemary Ballroom, the conference featured discussions on safety culture, teamwork, leadership, crew welfare, and Navitas’ long-term direction for improving vessel operations. Each session highlighted the company’s commitment to raising standards and ensuring a supportive environment for all crew members. Participants recognized the event as an important platform for strengthening communication, aligning expectations, and reinforcing the family-oriented culture that Navitas promotes across its fleet. The successful conclusion of the conference demonstrates Navitas’ continued dedication to building a highly professional, well-supported, and cohesive maritime workforce.

INTERTANKO Holds Seafarers’ Vetting Seminar in Manila
A specialized Seafarers’ Vetting Seminar organized by INTERTANKO is taking place in Manila, bringing together maritime professionals, shipping officers, and industry stakeholders to strengthen awareness on vetting and Port State Control (PSC) requirements. The seminar focuses on the critical role seafarers play in ensuring vessels meet international safety and compliance standards. Key discussions include current vetting trends, PSC priority areas, practical inspection preparation, and the human-element factors that influence a vessel’s operational performance. Industry experts are also expected to share real-world case studies and updated best practices to help crews and manning agencies improve readiness during vetting and PSC inspections. This Manila event highlights INTERTANKO’s continued commitment to supporting Filipino seafarers one of the world’s largest maritime workforces by providing updated knowledge essential to safe, compliant, and efficient tanker operations.

What is anchor? An anchor is a heavy device, typically made of metal, that is used to connect a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the vessel from drifting due to wind or current. Purpose ‣To Hold the Vessel in Place It secures the ship in a fixed location, especially when it is not at a dock or port. ‣To Prevent Drifting It stops the vessel from being carried away by wind, waves, or currents. ‣To Provide Safety in Emergencies In case of engine failure or rough weather, the anchor helps prevent the ship from drifting into danger. ‣To Assist in Positioning During Operations Useful for activities like dredging, diving, or repairs where stability is essential. 1. Fluke Anchor (Danforth) The Fluke anchor, also known as the Danforth anchor, is a lightweight, high-holding power anchor designed with two wide flat flukes that pivot on a shank. Purpose: It is ideal for anchoring in sandy or muddy bottoms, where its broad flukes can dig in deeply and hold firmly. Key Features: ‣Made of high-strength steel or aluminum ‣Lightweight and easy to handle ‣Excellent holding power relative to its weight ‣Commonly used on smaller vessels, yachts, and recreational boats 2. Plow Anchor (CQR) The Plow Anchor, commonly known as the CQR anchor (short for Coastal Quick Release), features a single plow-shaped fluke that pivots on a shank, resembling a farmer’s plow. Purpose: Designed to penetrate and bury itself in a variety of seabeds, it is widely used for general-purpose anchoring, especially in changing conditions Key Features: ‣Heavy-duty forged or cast steel construction ‣Hinged design allows it to adapt to shifting loads ‣Performs well in sand, mud, gravel, and some grassy bottoms ‣Often seen on cruising and commercial vessels 3. Bruce Anchor The Bruce anchor, also known as the Claw anchor, is a one-piece anchor with a claw-like shape designed to dig into the seabed and provide steady holding power. Purpose: Developed originally for offshore oil rigs, the Bruce anchor is now popular for small to medium recreational boats due to its reliable setting and holding capabilities. Key Features: ‣Made from forged or cast steel ‣One-piece construction with no moving parts ‣Performs well in sand, mud, and some rocky bottoms ‣Commonly used by cruising yachts and powerboats

FIRST COMPASS USED IN SHIP NAVIGATION
• A magnetized iron needle was rubbed with lodestone to create magnetic polarity. • The needle was placed on a small piece of cork, reed, or bamboo, allowing it to float freely. • This setup was placed in a bowl of water, reducing friction and stabilizing the movement. • The needle consistently aligned north–south, giving sailors a reliable reference during voyages. • This simple device became the earliest form of a marine water compass. When It Was Used • First appeared in 11th–12th century China during the Song Dynasty. • Adopted soon after by Arab navigators through trade routes. • Reached Europe by the 12th–13th century, widely used by Mediterranean and Atlantic sailors. • Became the foundation of early long-distance voyages across Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Why It Was the First Marine Compass • It was the first design stable enough to function on a moving ship, even during waves. • Provided direction when skies were cloudy, foggy, or stormy, when celestial navigation was impossible. • Allowed sailors to maintain a steady course in open ocean, not just coastal waters. • Its simplicity made it cheap, easy to build, and highly reliable for early maritime cultures. • This tool marked the beginning of true open-sea navigation, eventually evolving into the dry compass and modern gyrocompass.

Distress signals are official emergency indicators used by vessels to show that they are in grave and imminent danger and urgently require assistance. These signals are recognized worldwide under COLREGS Annex IV, ensuring that seafarers, coastal stations, and rescue authorities understand the situation instantly—no matter the language or location. Distress signals can be visual, sound-based, or radio-based, such as red star shells, flares, flames on deck, SOS, Mayday calls, smoke, gunfire at one-minute intervals, code flags, dye markers, radio alarms, or waving of arms. Each signal serves the same purpose: to alert others that the vessel or individuals are in a life-threatening emergency. Knowing these signals is essential for all maritime personnel, as they play a critical role in saving lives and enabling fast rescue operations.

PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the frontline defense of every seafarer working onboard. It protects crew members from physical, chemical, and environmental hazards while ensuring safe and efficient operations. Each piece of PPE serves a specific purpose that collectively reduces risk, prevents injury, and promotes a safety-first mindset onboard. 1. Protective Helmet Provides essential head protection against falling objects, impact, and accidental bumps in confined or elevated spaces. A mandatory requirement in all deck and engine operations. 2. Eye Wear (Safety Goggles) Shields the eyes from dust, debris, chemicals, sparks, and flying particles. Crucial during maintenance, grinding, chipping, or chemical handling. 3. Earmuff / Hearing Protection Reduces excessive noise levels from machinery, engines, and power tools. Helps prevent long-term hearing damage and fatigue. 4. Dust Mask (Respiratory Protection) Protects the wearer from inhaling dust, fumes, mist, and harmful airborne particles commonly encountered during painting, sweeping, or chemical tasks. 5. Safety Overalls Flame-retardant coveralls designed to protect the body from heat, sparks, oil splashes, and minor chemicals. High-visibility strips ensure the wearer remains easily seen. 6. Safety Gloves Provides hand protection against abrasions, cuts, chemical contact, and heat. Different glove types may be used depending on the task. 7. Safety Harness Critical for working aloft or in elevated areas. Prevents falls and secures the crew while working at height or over the side. 8. Safety Shoes Steel-toe or composite-toe footwear that protects the feet from heavy impacts, sharp objects, slips, and electrical hazards. Designed for tough marine environments.


The largest maritime community in the Philippines
© 2025 All Rights Reserved.
+63 (02) 8743 5810
customercare@marinoph.com
Agoncillo Building, 1580 Taft Ave, Ermita, Manila City, 1000 Metro Manila